Vibhute Prashant Chemistry blog
Thursday, 22 February 2024
Thursday, 18 January 2024
Sunday, 29 October 2023
Monday, 7 February 2022
Pericyclic reactions ,Photochemistry, Free radicals mcq M.Sc. SY Organic Chemistry
Photochemistry, Free radicals and Pericyclic reactions
Multiple Choice questions
a) 50:50
b) 93:7
c) 67:33
d) 60:40
Ans. (b)
2. Rearrangement of 1,4-Diene by photochemical process this rearrangement is called as
a) di-pi methane rearrangement
b) Zimmerman rearrangement
c) Both a and b
d) None of these
Ans. (c)
3. Irradiation of benzene gives
a) Benzvalene
b) Fulvene
c) Dewar benzene
d) All of the above
Ans. (d)
4. Ortho xylene on irradiation with photon of light gives
a) Only meta xylene
b) Only para xylene
c) Mixture of o,m,p-xylene
d) None of these
Ans. (c)
5. Ketene formation takes place in
a) Norrish Type-1
b) Norrish Type-2
c) Both a and b
d) None of these
Ans. (a)
6. β bond cleavage observed in which of the Photochemical process
a) Norrish Type-1
b) Norrish Type-2
c) Both a and b
d) None of these
Ans. (b)
7. α- bond cleavage observed in which of the Photochemical process
a) Norrish Type-1
b) Norrish Type-2
c) Both a and b
d) None of these
Ans. (a)
Wednesday, 2 February 2022
Symmetry properties of Molecular Orbital’s
Symmetry properties of Molecular Orbital’s:
· Molecular orbital’s of Ethene
In alkenes molecular orbital’s of ethene the carbon atoms are sp2 hybridized. The double bond between two carbon atoms is comprised of a σ-bond and π-bond. The former (C-C σ-bond) is formed by overlap of two sp2 orbital’s. The overlapping result’s in two π-molecular orbitals. In this case bonding π-orbital’s is formed by the overlap of in phase (same phase) of ‘p’ orbital and other π* anti bonding orbital’s arises from the interference between two p-orbital’s of opposite phases. These are designated by ψ1 and ψ2 respectively.
·
Molecular orbital’s of 1,3 butadiene:
In butadiene there are four p-orbital’s (ignore the σ-skeleton) and their combination gives four orbital’s having wave function ψ1, ψ2,ψ3,ψ4 with different energies of these ψ1 and ψ2 π-molecular orbital is bonding and ψ3 and ψ4 are antibonding molecular orbital’s. Molecular orbital is bonding if the number of bonding interactions is greater than number of nodes between nuclei and molecular orbital’s is antibonding, if the number of bonding interaction is less than the number of nodes between the nuclei.
Molecular Orbital’s of
1,3,5-hexatriene
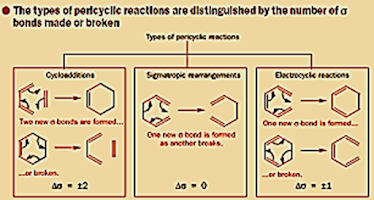
Classification of Pericyclic Reactions
Classification of Pericyclic Reactions
Introduction
Most of
the organic reactions proceeds in step wise manner. However there are certain reactions, which
proceed in a single concerted step via formation of a cyclic transition state
involving π or σ electrons.
OR
Electron moves round a circle and
there are no positive or negative charges on any intermediates-indeed, there
are no intermediates at all, such type of reaction is called Pericyclic reactions.
eg. Diels-Alder reaction.
The energy for Pericyclic reaction is supplied by heat in
thermally induced reaction or by ultraviolet in a photo-induced reaction.
Pericyclic reactions are highly stereospecific. Thermal and photo-chemical
process gives different products but specific stereochemistry.
Pericyclic reactions
do not involve ionic or free radical intermediates and so solvents and reagents
have no effect on the source of reaction.
Types of Pericyclic
reactions:
The three most common types of Pericyclic reactions are
1)
Cycloaddition
reaction
2)
Electro
cyclic reaction
3)
Sigma
tropic reaction
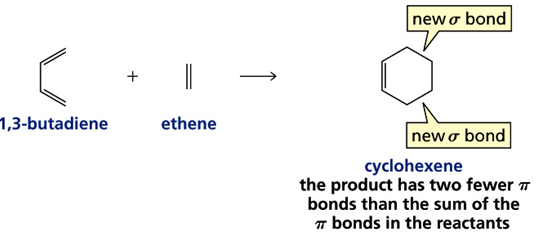
1) Cycloaddition Reactions
In these reactions two or more π electron system combines to form a ring. The reaction involve conversion of two π bonds into two sigma bonds (or reveres).
An example of cycloaddition reaction is well known as Diels-Alder reaction.
2)2)Electrocyclic Reactions
These are
reversible reaction in which a compound with conjugation double bond undergoes cyclization.
In this process two π electrons are used to form a σ-bond.
eg. 1,3,5 hexatriene
on heating gives 1,3 cycloheaxadiene
In the above illustration, an electrocyclic ring closer takes
place. The reverse of this process is an electrocyclic ring opening.
3) Sigmatropic Rearrangements
These
are concerted intermolecular rearrangements. In these rearrangements an atoms
(or group of atoms) shift from one position to another. The process involves
breaking of bond and forming of a new bond.
(But number of π bonds remains same)
eg. 3-methyl 1,5 hexadiene on heating gives 1,5
heptadiene.
Common example of sigmatropic reaction is Claisen rearrangement.
Types of Pericyclic reaction
Group Transfer Reaction: - a reaction in which one or more groups or atom transfer from one molecule. In this reaction both molecule are joined together by σ-bond.
Saturday, 29 January 2022
chemistry ebooks
B.Sc.Ty VI sem Thermodynamics
click on link Thermodynamics I notes
-
It has a lot of reference books I collected over the clg days It will be useful for you. please click on link for ebooks
-
Click on below link for Hand written notes f block elements
-
Photochemistry, Free radicals and Pericyclic reactions Multiple Choice questions 1. Stilbene on photochemical reaction gives cis stilbene ...